蘇美慈
Mei-Tzu Su

聯絡方式
☎️ +886-2-28267000 ext: 65371 (Lab) / 67267 (Office)
〒 R224, Department of Biotechnology and Laboratory Science in Medicine, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, No. 155, Sec. 2, Linong St., Beitou District, Taipei 112, Taiwan
學歷
- Ph.D., Graduate institute of Microbiology, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
- M.S., Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology, College of Life Sciences, Tzu-Chi University Hualien, Taiwan
- B.S., Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, College of Medical and Health Sciences, Fooyin University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
經歷
- Assistant Professor, Department of Biotechnology and Laboratory Science in Medicine, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2023/02-present
- Assistant Professor, Department of experimental Immunology, IDAC, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, 2018/04-2023/01
- Postdoctoral Fellow, Department of experimental Immunology, IDAC, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, 2017/07-2018/03
- Postdoctoral Fellow, Graduate institute of Microbiology, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2015/08-2017/04
研究主題
探討DNA聚合酶輔助因子BMRF1如何調控EB病毒溶裂期DNA複製以及參與病毒晚期基因的表現
在EB病毒溶裂期,BMRF1幫助病毒DNA聚合酶進行病毒DNA複製的同時亦會調控病毒尿嘧啶醣苷酶BKRF3進入細胞核,使溶裂期病毒核酸複製複合體順利形成以利病毒溶裂期DNA複製。此外,BMRF1也與染色質調控分子BRG1相互作用進而參與病毒晚期基因之轉錄調控。

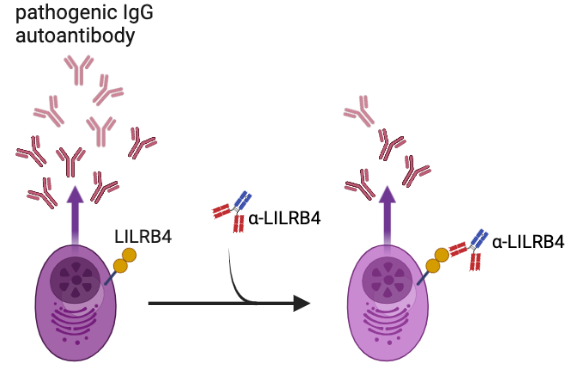
免疫抑制性受體Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor B4/glycoprotein 49B (LILRB4/gp49B) 調控自體抗體的生成
LILRB4 (小鼠直系同源物gp49B)大量表現於系统性红斑狼瘡(SLE)病人的漿細胞上。與東北大學研究團隊一起發現纖連蛋白(fibronectin, FN)是唯一可以同時接合人類LILRB4及小鼠gp49B的生理配體,其N端30kDa (FN30)為LILRB4/gp49B的結合位。利用抗體阻斷FN-LILRB4結合可減緩BXSB/Yaa狼瘡小鼠產生致病性自體免疫抗體。
LILRB4在腫瘤微環境中扮演的角色
LILRB4通過調節髓源抑制性細胞(MDSC)的M2極化和抑制MDSC分泌抗腫瘤miRNA來促進腫瘤轉移。我們更進一步證實抗LILRB4抗體之免疫治療可以抑制小鼠的肺癌細胞轉移,目前已申請國際專利並進入臨床研究。

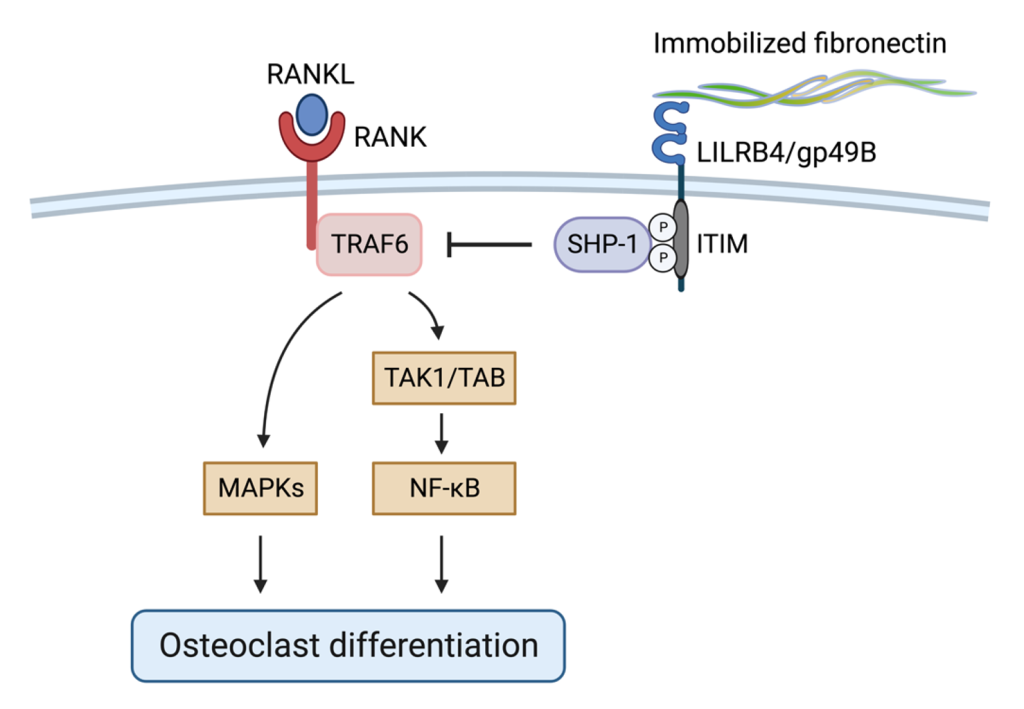
LILRB4/gp49B對骨穩態的影響
FN和 LILRB4/gp49B 的相互作用會增加SHP-1 的磷酸化並抑制破骨細胞(osteoclast)的生成。其機制為藉由磷酸化SHP-1與TARF6的相互作用來減弱 RANKL 誘導的 TRAF6/TAK1/NF-𝜅B/MAPK 訊息傳遞,進而抑制破骨細胞分化。
研究方向
- 腫瘤微環境的免疫重塑與治療策略開發
- 癌症相關病毒所誘發的免疫逃脫機制
- 免疫抑制受體在自體免疫疾病中扮演的角色
- 探討血液腫瘤疾病的危險因子對藥物治療之影響
研究室合作團隊與研究主題:
- 陽明交通大學 臨床醫學研究所 楊慕華教授 (頭頸癌治療&腫瘤微環境)
- 陽明交通大學 生化暨分生研究所 陳鴻震教授 (腫瘤微環境與細胞骨架)
- 陽明交通大學 腫瘤與免疫學研究中心 & 先進治療研發中心 張耀文 助理研究員 (腫瘤免疫治療&發炎與凝血機制&分子藥物開發)
- 陽明交通大學 生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 吳駿一 副教授 (腫瘤藥物開發)
- 台北榮民總醫院 血液科 劉嘉仁, 蔡淳光, 許德麟 醫師 (骨髓瘤&淋巴癌研究)
- 台大醫學院微生物研究所 (EBV病毒相關研究)
- 日本東北大學(免疫疾病與抗體藥物開發)
~~ 歡迎各領域學研單位、醫師團隊以及產業界夥伴攜手合作學術研究及產學開發 ~~
意者歡迎洽詢 張博士 yaowenchang@nycu.edu.tw
榮譽與獎項
- Professor Zhi-Zhong Yan Scholar Award, Chinese Society of Microbiology, Taiwan
- Travel Award, Scholarship for 39th Annual International Herpesvirus Workshop
- Academic Excellence Award, Tzu Chi University
- The Member of the Phi Tau Phi Scholastic Honor Society of the R.O.C.
研究著作
(†, co-first author; *, corresponding author)
- Chang YW, Hsiao HW, Chen JP, Tzeng SF, Tsai CH, Wu CY, Hsieh HH, Carmona SJ, Andreatta M, Di Conza G, Su MT, Koni PA, Ho PC, Chen HK, Yang MH. (2023). A CSF-1R-blocking antibody/IL-10 fusion protein increases anti-tumor immunity by effectuating tumor-resident CD8+ T cells. Cell Rep Med. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101154.
- Itagaki F, Nakatsuka K, Sakai H, Endo S, Su MT, Takai T. (2023). Fibronectin on target cells attenuates natural cytotoxicity of NK cells via myeloid immune checkpoint ILT3/LILRB4/gp49B. Int Immunol. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxad012.
- Kumata S, Notsuda H, Su MT, Saito-Koyama R, Tanaka R, Suzuki Y, Funahashi J, Endo S, Yokota I, Takai T, Okada Y. (2023). Prognostic impact of LILRB4 expression on tumor-infiltrating cells in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14991.
- Miyamoto S, Chiba T, Itoi S, Su MT, Takai T. (2023) LILRB4/gp49B Co-Localizes with Integrin via Fibronectin at Focal Adhesion Sites on Mast Cells. Tohoku J Exp Med. doi: 10.1620/tjem.2023.J001.
- Chao T.Y., Cheng Y.Y., Wang Z.Y., Fang T.F., Chang Y.R., Fuh C.S., Su M.T., Su Y.W., Hsu P.H., Su Y.C., Chang Y.C., Lee T.Y., Chou W.H., Middeldorp JM, Saraste J, Chen MR. (2023) Subcellular Distribution of BALF2 and the Role of Rab1 in the Formation of Epstein-Barr Virus Cytoplasmic Assembly Compartment and Virion Release. Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0436922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04369-22.
- Su M.T. †*,Ono K.†, Kezuka D.†, Miyamoto S., Mori Y., Takai T. (2022) Fibronectin-LILRB4 interaction negatively regulates osteoclastogenesis through inhibiting RANKL-induced TAK1 phosphorylation. Int Immunol. dxac051, https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxac051
- Itoi S., Takahashi N., Saito H., Miyata Y., Su M.T., Endo S., Fujii H., Harigae H., Sakamoto Y., Takai T*. (2022) Myeloid immune checkpoint ILT3/LILRB4/gp49B tether fibronectin with integrin on macrophages. Int Immunol. , dxac023, doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxac023.
- Takahashi N., Itoi S., Su M.T., Endo S., Takai T*. (2022) Co-localization of Fibronectin Receptors LILRB4/gp49B and Integrin on Dendritic Cell Surface. Tohoku J Exp Med. doi:10.1620/tjem.2022.J014.
- Su M.T. †*, Kumata S.†, Endo S., Okada Y., Takai T. (2022) LILRB4 promotes tumor metastasis by regulating MDSCs and inhibiting miR-1 family miRNAs. OncoImmunology; 11(1):2060907. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2022.2060907.
- Su M.T.†, Inui M.†, Wong Y.L., Takahashi M., Sugahara-Tobinai A., Ono K., Miyamoto S., Murakami K., Itoh-Nakadai A., Kezuka D., Itoi S., Endo S., Hirayasu K., Arase H., Takai T*. (2021) Blockade of Checkpoint ILT3/LILRB4/gp49B Binding to Fibronectin Ameliorates Autoimmune Disease in BXSB/Yaa Mice. Int Immunol.;33(8):447-458
- Tsai C.L.†, Sun D.S.†, Su M.T.†, Lien T.S.†, Chen Y.H., Lin C.Y., Huang C.H., King C.C., Li C.R., Chen T.H., Chiu Y.H., Lu C.C., Chang H.H*. (2020) Suppressed humoral immunity is associated with dengue nonstructural protein NS1-elicited anti-death receptor antibody fractions in mice. Sci Rep. 14;10(1):6294.
- Dai Y.C., Liao Y.T., Juan Y.T., Cheng Y.Y., Su M.T., Su Y.Z., Liu H.C., Tsai C.H., Lee C.P., Chen M.R*. (2020) The Novel Nuclear Targeting and BFRF1-Interacting Domains of BFLF2 Are Essential for Efficient Epstein-Barr Virus Virion Release. J Virol. 2020 Jan 17;94(3):e01498-19.
- Wong Y.L., Su M.T., Sugahara-Tobinai A., Itoi S., Kezuka D., Endo S., Inui M., Takai T*. (2019) Gp49B is a pathogenic marker for autoantibody-producing plasma cells in lupus-prone BXSB/Yaa mice. Int Immunol. 2019 May 21;31(6):397-406. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxz017.
- Chang Y.W., Tseng C.P., Lee C.H., Hwang T.L., Chen Y.L., Su M.T., Chong K.Y., Lan Y.W., Wu C.C., Chen K.J., Lu F.H., Liao H.R., Hsueh C., Hsieh P.W*. (2018). β-Nitrostyrene derivatives attenuate LPS-mediated acute lung injury via the inhibition of neutrophil-platelet interactions and NET release. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Apr 1;314(4):L654-L669.
- Lin G.L., Chan H, Chang H.H., Chen P.K., Su M.T. and Sun D.S.* (2017). Suppressive effect of dengue virus envelope protein domain III on megakaryopoiesis. Virulence. 16:1-13.
- Su M.T., Yang P.W., Wang Y.T., Yang M., Lee C.P., Tsai C.H. and Mei-Ru Chen*. (2017). The The SWI/SNF Chromatin Regulator BRG1 Modulates the Transcriptional Regulatory Activity of the Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Polymerase Processivity Factor BMRF1. J Virol. 91, pii: e02114-16.
- Chang C.W., Lee C.P., Su M.T., Tsai C.H., and Chen M.R*. (2014). BGLF4 Kinase Modulates the Structure and Transport Preference of the Nuclear Pore Complex to Facilitate Nuclear Import of Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Proteins. J Virol.;89, 1703-18.
- Su M.T., Liu I.H., Wu C.W., Chang S.M., Tsai C.H., Yang P.W., Chuang Y.C., Lee C.P., and Chen M.R*. (2014). Uracil DNA glycosylase BKRF3 contributes to Epstein-Barr virus DNA replication through physical interactions with proteins in viral DNA replication complex. J Virol.;88, 8883-8899.
- Lee C.P., Liu P.T., Kung H.N., Su M.T., Chua H.H., Chang Y.H., Chang C.W., Tsai C.H., Liu F.T., and Chen M.R*. (2012). The ESCRT machinery is recruited by the viral BFRF1 protein to the nucleus-associated membrane for the maturation of Epstein-Barr Virus. PLoS pathogens 8, e1002904.
- Chang Y.H., Lee C.P., Su M.T., Wang J.T., Chen J.Y., Lin S.F., Tsai C.H., Hsieh M.J., Takada, K., and Chen M.R*. (2012). Epstein-Barr virus BGLF4 kinase retards cellular S-phase progression and induces chromosomal abnormality. PloS one 7, e39217.
- Chen L.W., Su M.T., Chen P.H., Liu W.C., and Hsu C.M.* (2011). Hypertonic saline enhances host defense and reduces apoptosis in burn mice by increasing toll-like receptors. Shock 35, 59-66.
實驗室活動


實驗室成員




